Apache Spark - HyperIoT Framework Docs
Title_Documentation
Documentation

Knowledge Base Display
Apache Spark
The HyperIoTSparkManager project is responsible for the interaction between HyperIoT and Spark. Currently, the supported version of Spark is 2.4.5.
The project follows the classic split dictated by HyperIoT, which is why the following chapters will focus on the operations exposed by the api module, the link that Spark jobs have with HyperIoT jobs, and configurations.
Spark Manager System Api Interface
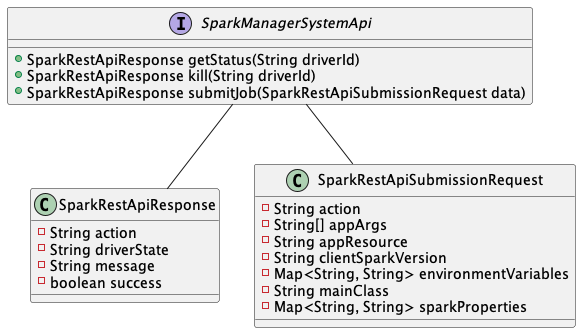
Spark Manager System Api Interface
The interface exposes methods for job submission and termination, as well as for querying the state of job execution. Each of the indicated operations returns an instance of the SparkRestApiResponse type, containing information about the requested action and the job that the latter was executed. This is the response provided by the Spark Hidden REST API: each of the methods, in fact, interfaces behind the scenes with that API. The link between the interface’s operations and Spark’s REST APIs is also evident from the argument provided when submitting the job, namely an instance of the SparkRestAtpiSubmissionRequest class: this contains mandatory information for the job to be executed correctly (refer to the technical analysis of integration with Spark for more details).
HyperIoTSparkJob Class
The HyperIoTSparkJob class represents the link between HyperIoT, Spark, and the Quartz scheduler. It is the example of a specific job (i.e., executed on Spark) that can be scheduled through the platform, and whose execution is managed, precisely, by Quartz.
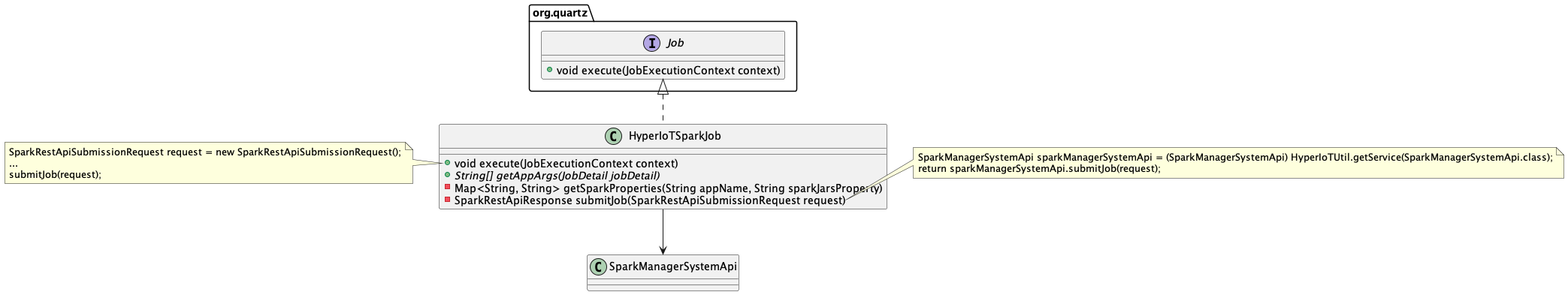
Spark Job Class
The execute method is invoked by Quartz at the time the job’s cron expression is satisfied. As can be seen in the note above in the class diagram, the execute method invokes the private submitJob method, which interfaces with the SparkManagerSystemApi for the job submission request to Spark.
Configurations
In the Karaf distribution there is the file en.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.cfg for module configuration.
The properties in the file follow:
| Property | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.client.version | 2.4.5 | Spark Client Version |
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.driver.supervise | false | If true, it automatically restarts the driver if it ends with state other than 0. |
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.env.loaded | 1 | It is not a property of Spark, nor a system property of Java, but an environment variable of the operating system. It is simply used in one of the scripts used for command-line execution (e.g., load-spark-env.sh on Linux and load-spark-env.cmd on Windows) to make sure that spark-env.* is executed only once. You can assign any value to it; the script just checks whether it is empty or not. (This is a typical property of the Spark Hidden REST API: if not specified, the job submission will fail.) |
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.master.hostname | http://spark-master | Spark Master URI |
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.master.tcp.port | 8090 | Spark Master TCP Port |
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.master.rest.api.port | 6066 | TCP port exposed by the Spark Master for Hidden REST API invocation. |
| it.acsoftware.hyperiot.sparkmanager.spark.submit.deploy.mode | cluster | Spark’s mode of execution |
